Chronic diseases can last for decades and require a disciplined approach to medication administration plus a lifestyle change. Among the most common chronic ailments are cardiovascular disease, diabetes type 2, respiratory diseases (asthma), and cancer 3 . Globally, one-third of adults suffer from one or multiple chronic conditions. Three in five global deaths are due to diabetes, cancer, chronic respiratory illnesses, and cardiovascular disease 4 . Medication adherence is defined by the World Health Organization as “the degree to which the person’s behavior corresponds with the agreed recommendations from a health care provider”. Approximately 50% of patients with chronic conditions are estimated to not adhere to their prescribed medications 5 . Inadequate medication adherence leads to ineffective treatment and undesired consequences like delayed recovery and an increase in hospitalization. Suboptimal use of medications in patients with chronic conditions is generally due to lower health literacy, ineffective communication between patient and health care practitioner, adverse effects, complex medication schedules, and incomplete awareness about the drug 5 . Therefore, technology that can assist chronic disease patients in medication management, health monitoring, and generating health awareness is acutely required.
Smartphones have become an inseparable part of our lives and mobile applications are their key component. Mobile apps are computer programs or software installed on mobile electronic devices to support a variety of features and applications 1 .The advent of mobile internet services and smartphones has generated a huge population of patients who can be approached through mobile to drive adherence to medication 1 . These health apps can also help to enhance lifestyle and provide targeted digital material to generate health literacy. Therefore, a number of health apps – upwards of 3,00,00 – are available on various repositories, of which about 10,000 focus on medication adherence 6 . A recent study providing an overview of mobile health applications analyzed 420 free apps that focused on medication management. These applications could be divided into three major sub-groups based on the tools and services provided such as medication reminders, behavioral change interventions, and health education. The majority of these apps are developed by software companies and many are freely available, while some are paid. Among both freely available and paid apps, only a few are developed in association with healthcare practitioners or come from academic background 7 .
In the present technology-driven world digital interventions like mobile apps, SMS (short message service) messages, wearable and ambient sensors, email, social media, and interactive websites play an important role in every aspect of our lives. Mobile health has now become an integral part of healthcare services and is defined as digital healthcare delivery tools on mobile devices. Mobile health applications can help in delivering health information, collecting patient data, or supporting other healthcare-related hardware 6 . Mobile apps are easy to use, cheap, and can improve the management of diverse chronic diseases. They can enhance adherence by helping as a medication reminder, medication monitoring, clinical decision support, feedback from physicians, setting up appointments, and sharing data with HCPs 1 . For example, apps designed for diabetes can help in diabetes management by monitoring physical activity, nutrition, blood glucose testing, medication or insulin dosage, and providing health feedback as well as information 8 .
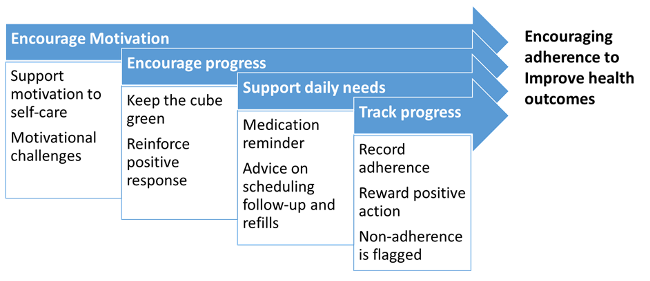
The “my a:care” app is a pioneering mobile application that healthcare professionals can recommend to their patients for supporting medication adherence and improving health outcomes. The uniqueness of this app lies in employing established behavioral science methods to tackle non-adherence in patients. The “my a:care” app enables patients to take small, manageable steps while rewarding positive actions to bring lasting behavioral changes 9 .
The my a:care app is a personal coach:

Dosecast is a medication management app that tracks and improves medication adherence. The app allows patients to take a photo of their pill and upload it because the app has a drug database so it is simple to select the appropriate medication when setting a reminder and it keeps track of the amount of each medication, sending a refill notice when patients are getting low 11 .
App features:
The Round Health app provides all of the vitamins and medicines in one place. The app offers discreet, continuous reminders that go beyond awkward phone alarms. Round Health is a good choice for older patients or those who need a simple feature set to use technology to manage their adherence 12 .
Other features include:
Table 1: Feature comparison between the my a:care, Dosecast, and Round Health
| Features | Abbott’s my a:care app | Montuno Software’s Dosecast | Circadian Design’s Round Health |
| App website | ✓ | – | – |
| Tracking | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Medication Reminders | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Appointments | ✓ | ✓ | – |
| Administration | ✓ | – | – |
| Motivational coaching | ✓ | – | – |
| Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Health tips | ✓ | – | – |
| Data Sharing | ✓ | ✓ | – |
| Chats/Conversations | ✓ | ✓ | – |
| Feedbacks | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Cost (USD) | 0 | 0(Basic)+ ~$4(Premium) | 0 |
| Audience | Patients & HCPs | Patients | Patients |
In the current technology-driven world, mobile applications play an important role in every aspect of our lives. Particularly in healthcare, apps can help to monitor health conditions, keep track of medications and share health records remotely with the physician. Mobile apps can help to ensure adherence by working as reminders, suggesting lifestyle changes, and elevating health literacy specifically in chronic disease management.
“Better medication management and better adherence will result in better health system performance on quality and cost metrics.” – Jonathan Niloff, M.D., vice president, and chief medical officer at McKesson
1. Peng Y, Wang H, Fang Q, et al. Effectiveness of Mobile Applications on Medication Adherence in Adults with Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. Apr 2020;26(4):550-561. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2020.26.4.550
2. Perez-Jover V, Sala-Gonzalez M, Guilabert M, Mira JJ. Mobile Apps for Increasing Treatment Adherence: Systematic Review. J Med Internet Res. Jun 18 2019;21(6):e12505. doi:10.2196/12505
3. Reynolds R, Dennis S, Hasan I, et al. A systematic review of chronic disease management interventions in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. Jan 9 2018;19(1):11. doi:10.1186/s12875-017-0692-3
4. Hajat C, Stein E. The global burden of multiple chronic conditions: A narrative review. Prev Med Rep. Dec 2018;12:284-293. doi:10.1016/j.pmedr.2018.10.008
5. Brown MT, Bussell JK. Medication adherence: WHO cares? Mayo Clin Proc. Apr 2011;86(4):304-14. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0575
6. Backes C, Moyano C, Rimaud C, Bienvenu C, Schneider MP. Digital Medication Adherence Support: Could Healthcare Providers Recommend Mobile Health Apps? Front Med Technol. 2020;2:616242. doi:10.3389/fmedt.2020.616242
7. Ahmed I, Ahmad NS, Ali S, et al. Medication Adherence Apps: Review and Content Analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Mar 16 2018;6(3):e62. doi:10.2196/mhealth.6432